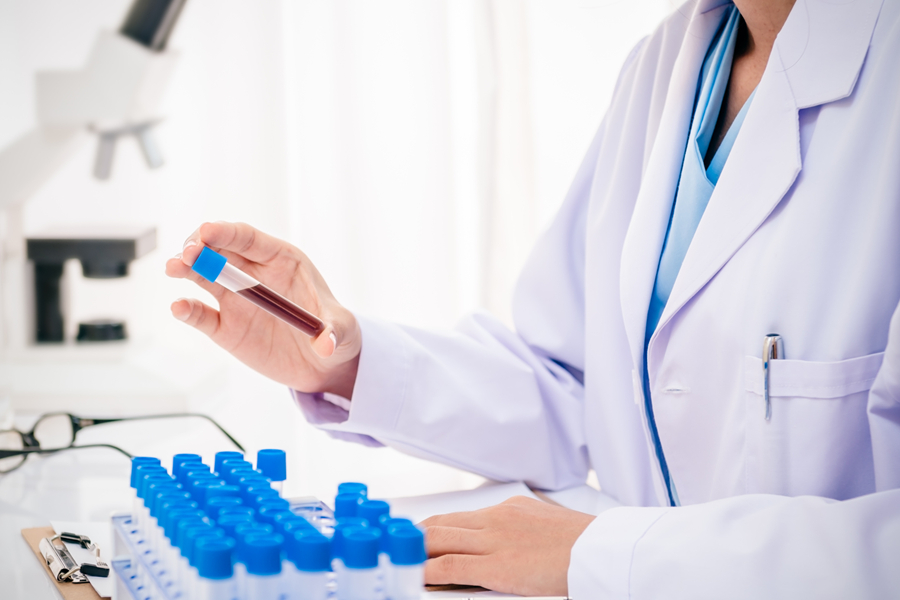
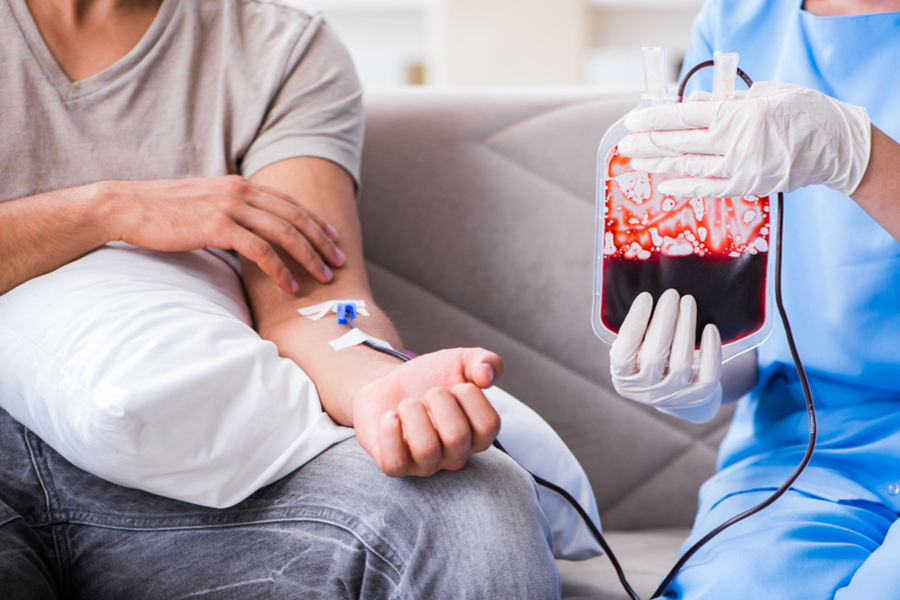
The diagnosis of thalassemia typically begins with a physical exam and family history review followed by a blood test to measure hemoglobin levels. If these tests show signs of abnormal hemoglobin levels, your doctor may order additional tests such as genetic testing or a bone marrow biopsy to confirm a diagnosis.
Treatment for thalassemia depends on its severity but may include regular blood transfusions, iron chelation therapy to remove excess iron buildup, medications, or even stem cell transplantation in some cases. In addition, lifestyle changes such as eating a balanced diet low in fat and high in fiber can help reduce symptoms associated with this condition.
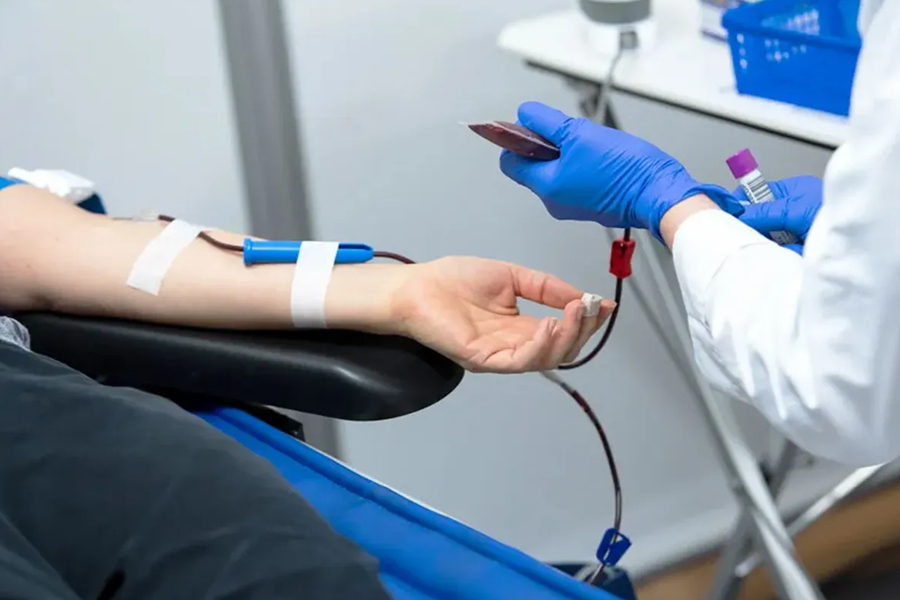
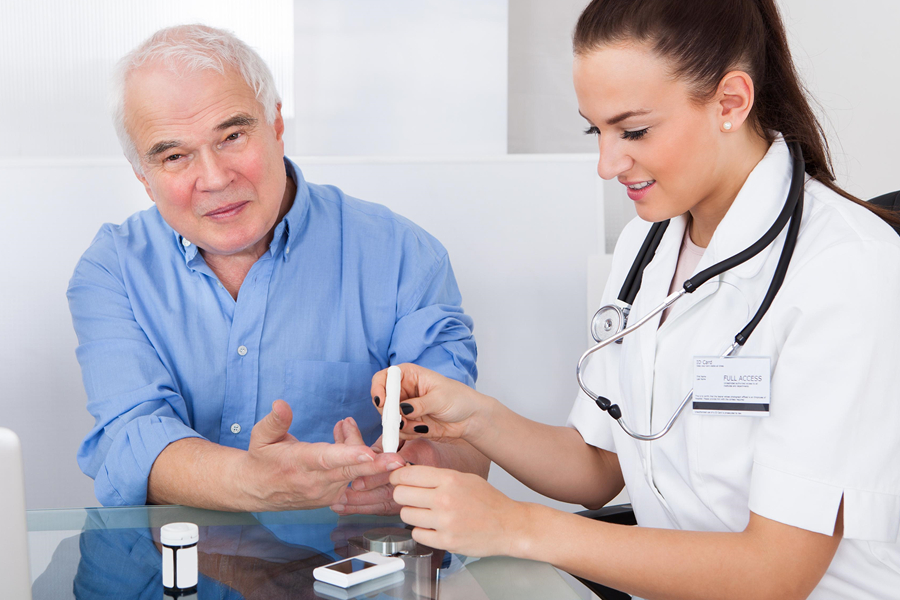
It’s important for people with thalassemias to be monitored closely by their doctors so any complications can be addressed quickly before they become more serious or life-threatening. Regular visits for checkups should include routine laboratory testing including CBC complete blood count and electrolytes as well as monitoring for signs or symptoms that could indicate complications related to iron overload due to frequent transfusions or other treatments used to manage this condition.
Overall, understanding what causes Thalessemiad is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment planning so that individuals living with this condition can lead healthier lives despite its challenges. With adequate care management including access to appropriate medical specialists when needed along with lifestyle modifications focused on nutrition, exercise, stress reduction techniques etc., those living with Thalessemiad can live longer healthier lives free from serious complications related to their condition which ultimately leads them closer towards achieving optimal health outcomes overall!